https://pussmoth.com/la-migracion-de-las-mariposas-hacia-florida/
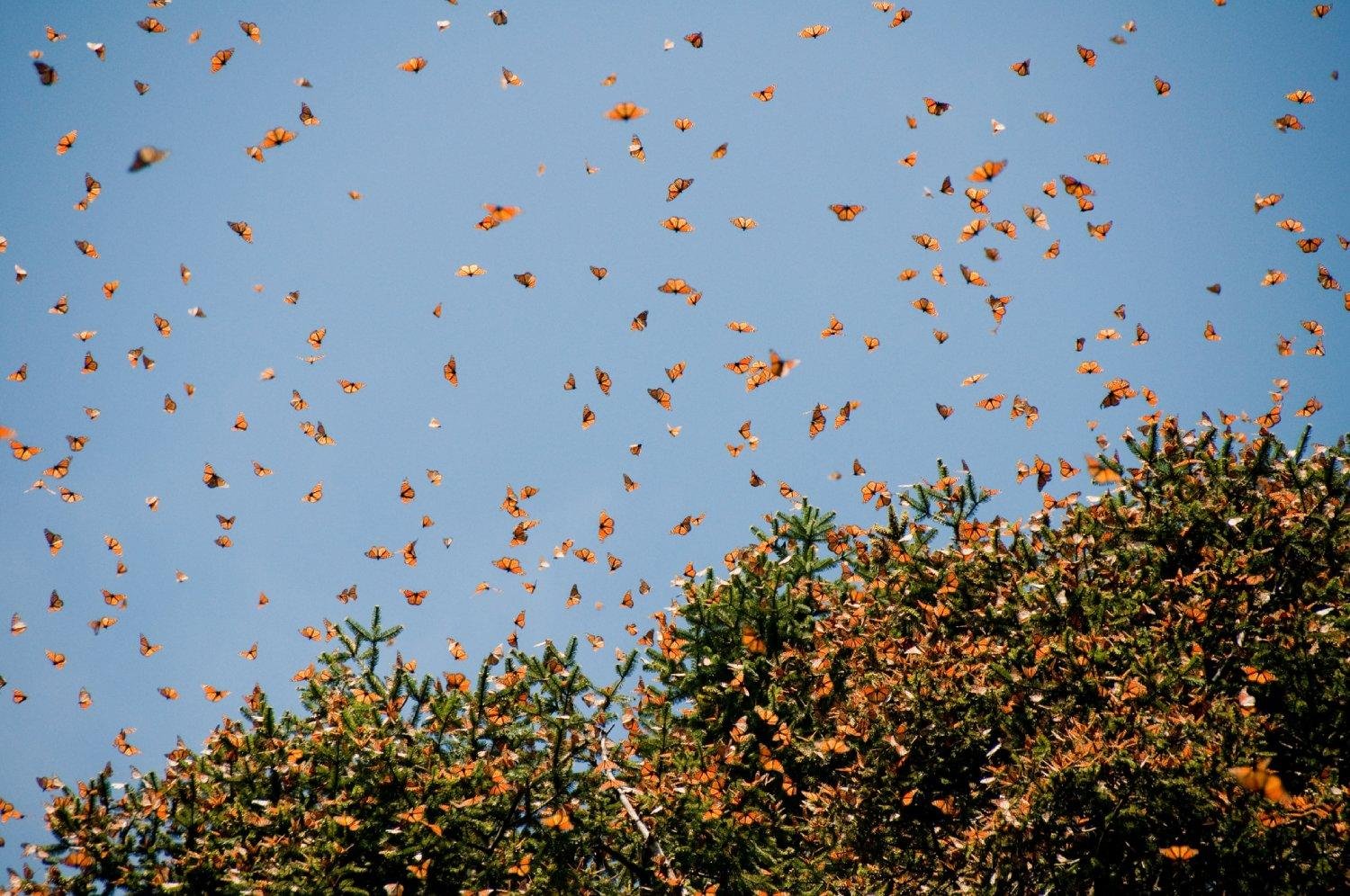
Butterfly migration is a fascinating natural phenomenon that has captivated the attention of scientists, ecologists, and nature lovers alike. One of the most notable migrations is that of the monarch butterfly (Danaus plexippus), which travels from North America to Florida and other areas in the south. https://pussmoth.com/la-migracion-de-las-mariposas-hacia-florida/ This article explores the most important aspects of the migration.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. What is Butterfly Migration?
Migration is defined as the seasonal movement of animals from one place to another in search of better environmental conditions, such as food or habitat. In the case of butterflies, this phenomenon is particularly noticeable in monarch butterflies, which undertake a journey of thousands of kilometres. This journey takes place in several stages and is an impressive spectacle of nature.
2. Migratory Route of the Monarch Butterflies
Monarch butterflies migrate from the northern United States and Canada southward, reaching as far as Mexico, where they spend the winter in pine forests. However, many of these butterflies also head to Florida and other areas of the southern United States. During this journey, monarchs can cover up to 3,000 miles (about 4,800 kilometers), and their migration usually occurs between August and November, when the weather begins to cool.
2.1 Stages of Migration
- Beginning of Migration : Migration begins in the north, where butterflies prepare for the long journey by beginning to feed on nectar and increasing their fat reserves.
- Route and Rest : As they head south, butterflies make stops in areas rich in nectar and shelter, where they can rest and feed.
- Arrival in Florida : Some of these butterflies arrive in Florida, where they will find a warmer climate and abundant food, ideal for continuing their life cycle.
2.2 Factors that Influence Migration
Several factors influence the migration of monarch butterflies:
- Climate : Changes in temperature and food availability are key drivers for initiating migration.
- Photoperiod : The daylight cycle affects the reproductive behavior of butterflies and their migratory drive.
- Nectar and Resources : The availability of flowers and host plants, such as milkweed (Asclepias), is crucial for survival during the journey.
3. Importance of Butterfly Migration
Monarch butterfly migration is not only an impressive spectacle, but also plays an important role in the ecosystems where it occurs. Below are some of the key contributions:
3.1 Pollination
Butterflies are essential pollinators that contribute to the fertilization of numerous plants, including many agricultural species. Their pollination activity supports biodiversity and ecosystem health.
3.2 Ecological Indicators
Monarch butterflies are considered ecological indicators. Their presence or absence can provide information about the health of the environment. Declines in their populations can signal problems in the ecosystem, such as habitat loss or overuse of pesticides.
3.3 Cultural Connection
Butterfly migration has captured the imagination of many cultures and has been the subject of scientific study. In many communities, butterflies are a symbol of transformation and change.
4. Threats to Butterfly Migration
Despite their amazing journey, monarch butterflies face numerous threats that have contributed to their decline in recent decades:
4.1 Habitat Loss
Urbanization, intensive agriculture and land use change have led to the loss of critical habitat for butterflies, affecting their ability to find nectar and shelter.
4.2 Use of Pesticides
The use of pesticides and herbicides in agriculture has reduced populations of host plants, such as milkweed, that are crucial to the survival of monarch larvae.
4.3 Climate Change
Climate change is altering migration patterns and affecting resource availability along migration routes, which may have a negative impact on butterfly populations.
5. How to Protect Monarch Butterflies
Conservation of monarch butterflies and their habitat is crucial to ensure they continue to migrate. Here are some ways individuals and communities can help:
5.1 Planting Native Species
Planting milkweed and other native species in gardens and urban landscapes can provide food and shelter for butterflies on their migration route.
5.2 Reduce Pesticide Use
Opting for more sustainable and natural pest control methods can help protect butterflies and other pollinators in the garden.
5.3 Support Conservation Initiatives
Participating in conservation programs and projects dedicated to protecting butterflies and their habitat can have a significant impact.
5.4 Educate the Community
Education about the importance of butterflies and the challenges they face is key to generating support and action around their conservation.
6. Conclusion
The migration of butterflies to Florida is a stunning natural phenomenon that highlights the beauty and fragility of life. Protecting monarch butterflies is essential not only to their survival, but also to the health of our ecosystems. Through education, conservation, and community action, we can help ensure that these incredible creatures continue their